논문 리뷰 : SCAN: Learning to Classify Images without Labels
이번 논문은 그동안 리뷰했던 Image Representation Learning을 사용하여 downstream task로 clustering을 진행한 SCAN(Semantic Clustering by Adopting Nearest neighbors)이라는 논문입니다. Unsupervised Image classification 이라는 흔치않은(?) task를 수행했다고 합니다.
Intro
- Unsupervised Image Classification
- Two-step approach(not end-to-end)
- First : “Self-supervised task from representation learning is employed to obtain semantically meaningful features.”
- Second : “We use the obtained features as a prior in a learnable clustering approach.”
위 네 가지로 논문을 요약할 수 있을 것 같습니다. Unsupervised Image Classification을 수행하였고, 이 과정을 Representation Learning, clustering으로 나누어 구성하였습니다. 논문의 Experiment 부분을 봤을 때, Unsupervised Image Classification은 evaluation에서 헝가리안 매칭 알고리즘을 사용한다는 점에서 단순 Clustering과 구분된 표현인 것 같습니다.
Prior work
Feature Learning with clustering
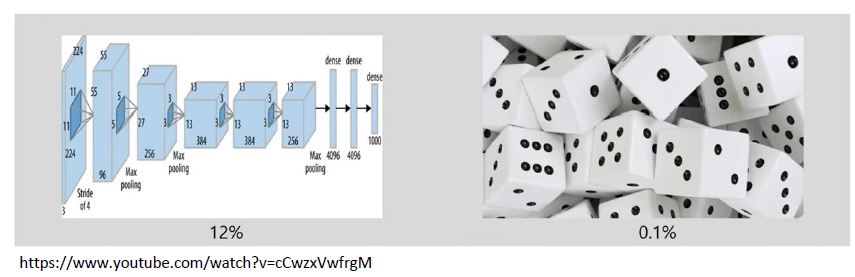
논문에서 Deep Clustering을 주요 비교 대상으로 삼고 있습니다.
“The good performance of random convnets is intimately tied to their convolutional structure which gives a strong prior on the input signal. The idea of this work is to exploit this weak signal to bootstrap the discriminative power of a convnet.”
Deep Clustering은 위와 같은 아이디어로 random initialized CNN의 output을 clustering한 결과를 supervision을 사용하여 이미지의 representation을 학습하는 방법을 제안하였습니다. 이러한 학습방식은 학습 초반에 정확하지 않은 clustering 결과를 supervision으로 사용한다는 문제를 가지고 있는데 SCAN에선 이를 지적하며 이러한 Clustering degeneracy 문제를 개선한 것이 주요 contribution이라 말합니다.
Method
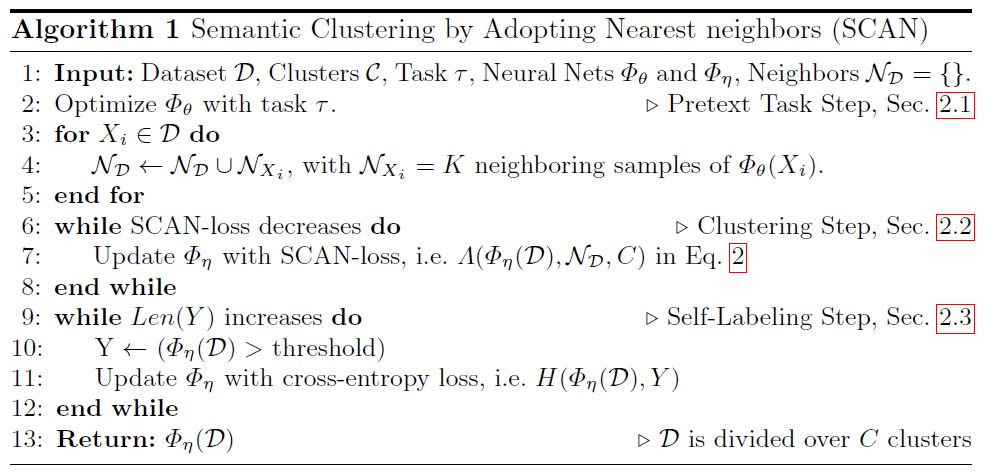
SCAN의 학습과정은 크게 Pretext task, Scan Clustering, Self-labeling으로 나눠집니다.
Pretext task
“We employ representation learning as a means to obtain a better prior for semantic clustering.”
먼저, pretext task는 Image Representation Leanring의 선행 연구인 SimCLR, MOCO를 그대로 사용합니다. Image transformation에 따라 변하지 않는 semantic feature를 학습하기 때문에 두 방법을 사용했다고 하고, contrastive learning에 사용된 instance discrimination 방식이 결과적으로 같은 class 간의 거리를 상대적으로 가깝게 하기 때문에 이를 Clustering에 사용하기 위함입니다.
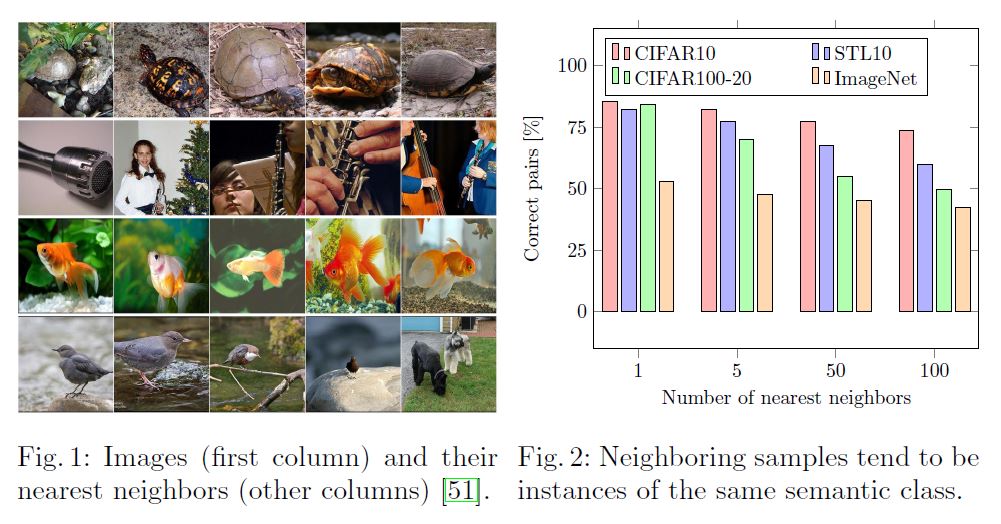
Scan Clustering
pretext 단계에서 학습한 image representation을 사용해서 clustering 단계에선 아래의 Loss를 통해 clustering을 학습합니다.
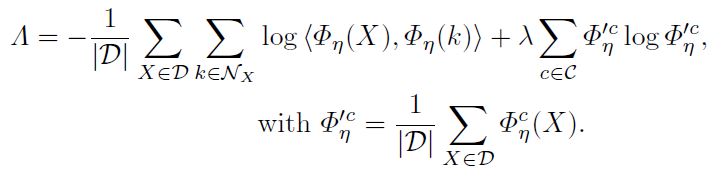
Loss의 앞 부분은 이미지별 nearest neighbor와의 similarity를 최대화(-1을 곱해서 최소화)하여 같은 cluster로 예측하도록 하고 있고, 뒷 부분은 cluster별 entropy합을 최대화 하고자 합니다. cluster의 개수는 미리 정해야하는 hyperparameter이며 논문에선 데이터를 구성하는 class 수는 이미 알고 있다는 가정하에 class 수와 같은 개수로 설정하여 실험하고 있습니다.
Self-labeling
Self-labeling 단계에선 clustering 잘 된 이미지들을 confidence를 기준으로 선정하고, cluster 결과를 pseudo label로 할당하여 supervised learning을 진행합니다. 이를 통해 잘 학습된 이미지들을 최대한 활용하고, nearest neighbor를 같은 cluster로 할당하면서 발생한 noise를 바로잡을 수 있다고 논문에선 말합니다.
아래는 전체 학습과정을 Algorithm으로 나타내고 있습니다.
Experiments
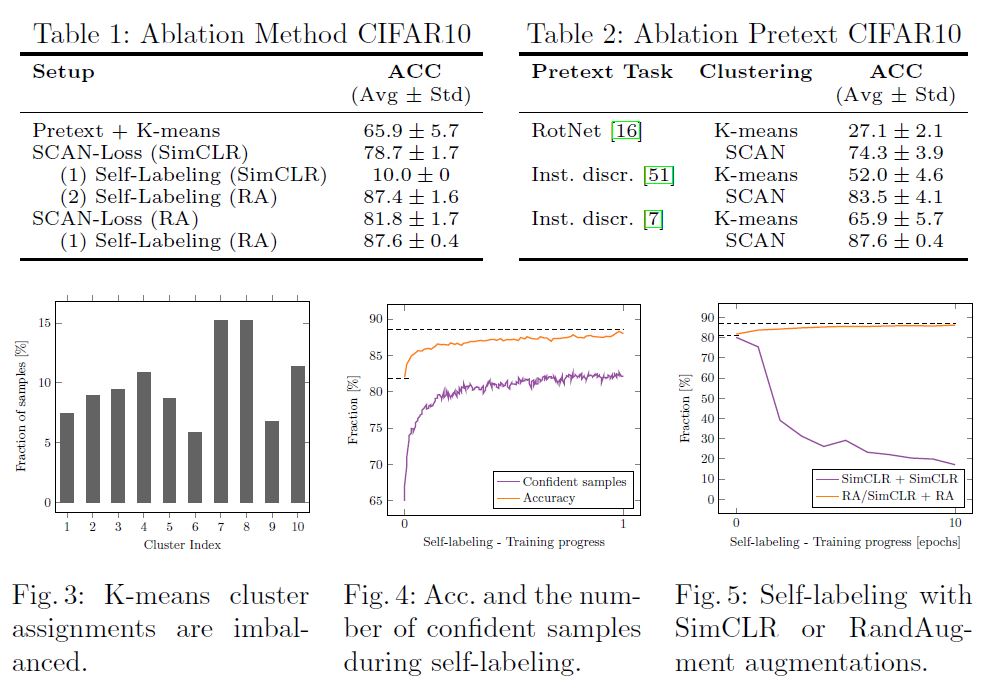
위는 Cifar-10 데이터에 대해 ablation study를 수행한 결과입니다. Table1을 보면 Pretext만 학습하고 K-means를 한 경우에도 기존 연구들에 비해 높은 성능을 확인하였고, Scan clustering과 Self-labeling 각각을 추가학습할 때마다 유의미한 성능향상을 보여줍니다. 또한, Self-labeling 단계에선 잘 clustering 된 소수의 이미지를 학습하기 때문에 좀 더 강한 augmentation을 사용해야 성능향상이 됨을 Fig.5를 통해 알 수 있습니다.
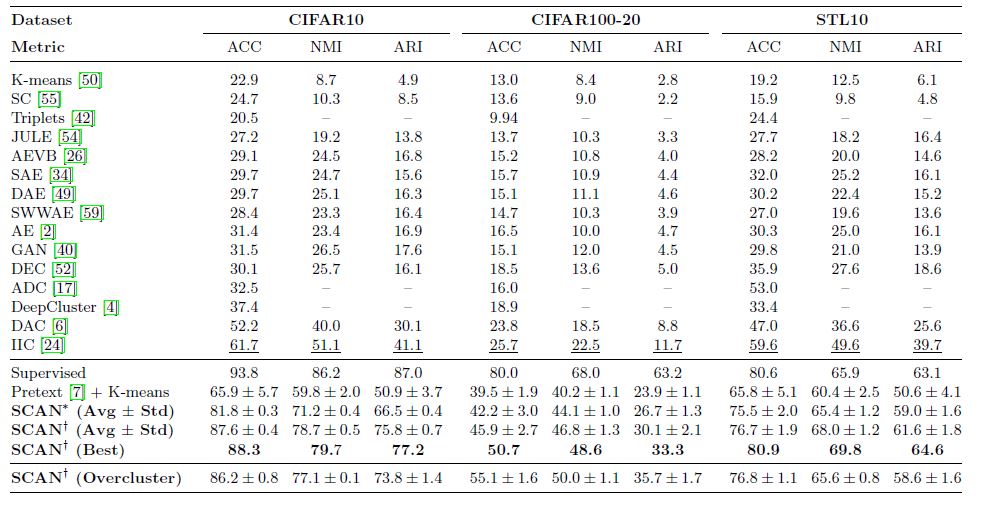
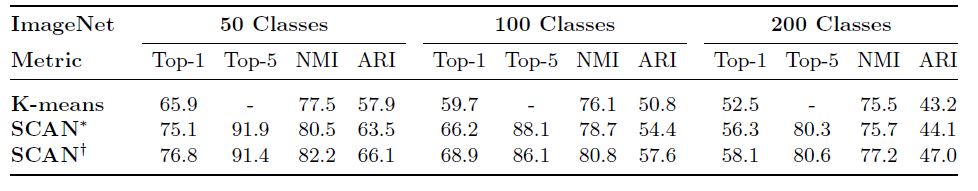
위 두 결과는 작은 크기의 이미지로 CIFAR10, CIFAR100-20, STL10, 큰 이미지로 ImageNet 데이터셋을 각각 사용했을 때의 실험결과입니다. CIFAR10 이나 STL10 데이터셋의 경우 Supervised 성능과도 크게 차이 나지 않는 결과를 보였고, ImageNet의 경우 50, 100, 200으로 전체 class 중 일부만 사용했음에도 성능상 아직 개선될 여지가 많을 것으로 보입니다.
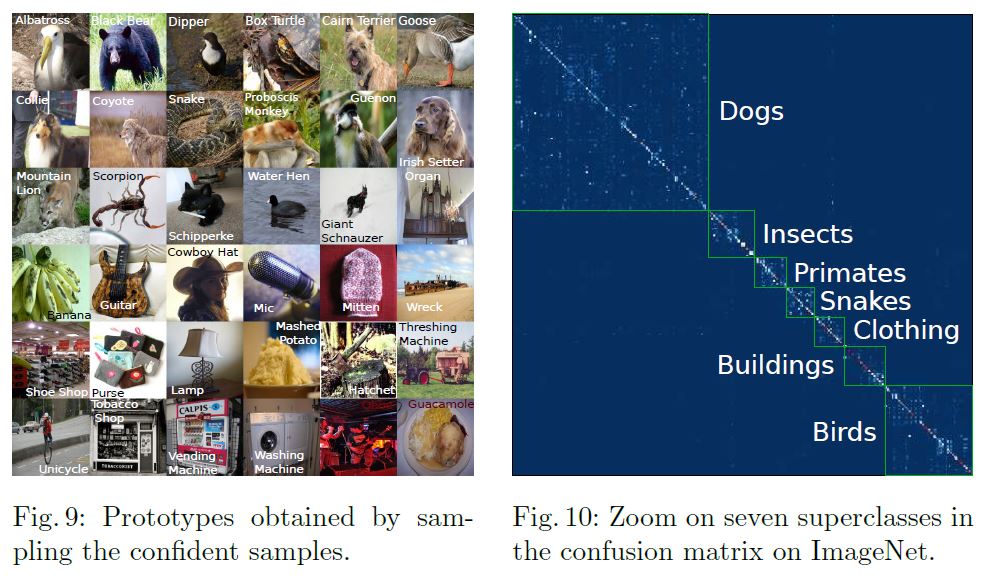

위 그림이 개인적으로 의미있다고 생각하는 결과인데, 왼쪽은 cluster별로 confidence가 높은 이미지들인데 눈으로 보기에도 각 class를 대표할 수 있을만한 명확한 이미지들이 뽑힌 것을 볼 수 있고, 오른쪽은 결과가 서로 많이 섞인 cluster들이 실제로 상위 class로 묶일 수 있음을 보여줍니다. 즉, Nearest neighbor를 통해 clustering하는 과정이 class 단위에서도 semantic한 공통점이 있는 이미지들을 더 잘 뭉쳐준다고 볼 수 있을 것 같습니다. 이 논문은 unsupervised image clustering이라는 task를 target으로 하고 있지만, feature level에서 인접한 이미지들, 즉 cluster 정보가 self supervision으로 사용될 수 있음을 어느정도 보여주면서 SwAV같은 Self supervised learning 연구들의 근간이라고 볼 수도 있지 않을까 생각합니다.
Reference
paper :
SCAN: Learning to Classify Images without Labels
Deep Clustering for Unsupervised Learning of Visual Features
A Simple Framework for Contrastive Learning of Visual Representations
Momentum Contrast for Unsupervised Visual Representation Learning
Improved Baselines with Momentum Contrastive Learning